Data Privacy Compliance Conundrum – Why is it Important to Businesses?
Do Businesses Protect Our Secrets From Data Thieves?
The Avalanche of Data Privacy Compliance
Data privacy compliance is the fine line that an organization must walk when dealing with data. This compliance regulation protects consumers in various countries by ensuring proper data handling.
It is the area of data management concerned with the handling of personal data in accordance with data protection laws, regulations, and general privacy best practices. Setting access controls to protect information from unauthorized parties, obtaining consent from data subjects when necessary, and maintaining data integrity are all part of ensuring data privacy.
We live in an era of unprecedented regulatory change and growth, with stringent data privacy regulations emerging globally at a rapid pace. The need to protect personal data has become mission critical across all industry sectors, posing compliance challenges as well as opportunities for gaining a competitive advantage, maintaining brand loyalty, and safeguarding customer trust.

As a result, data privacy is gradually becoming a top priority for businesses. Failure to comply with data privacy regulations can result in significant financial losses. Consider legal action, substantial financial penalties, and reputational damage. Data privacy is a subset of the larger topic of data governance. Organizations must understand what data they have, where it is stored, how it flows through their IT systems, and how it is used. Best practices in data governance enable organizations to maintain data integrity and trust in their data.
Defining Sensitive Data
Today any data, from a company’s earnings to sales figures or product roadmaps, may be sensitive. Information about people — personal data about any identified or identifiable individual — is among the most sensitive data. Almost anything can be considered personally identifiable information (PII).
Personal information isn’t always as obvious as a name or Social Security number. Other identifiers, such as an IP address or cookie information, are sometimes used. Personal data is data that can be used to identify an individual based on a data field or record.
The value of data privacy in today’s business environment cannot be overstated. Personal data, such as credit card information or personal health information, is subject to data privacy laws in the majority of the world.
Sensitive data is defined legally as “information that must be protected against unauthorized disclosure.” It is not only a legal obligation, but also ethically sensible, to protect such information and limit access to such information, especially when it concerns a person’s individual privacy and property rights.
Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty refers to the idea that data is subject to the laws of the country where it is collected. For example, the Schrems II ruling in July 2020 determined that, under GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), consumer data for customers in the EU must be hosted on servers within the EU’s borders.
Consider data sovereignty as a means of ensuring that user data remains close to home for its own protection. Governments hope to prevent their citizens’ data from falling into the wrong hands by dictating where it can be stored and processed. When evaluating cloud service providers, data sovereignty becomes critical. GDPR compliance, or future regulations, may necessitate the storage of specific data on servers in specific jurisdictions.
In terms of data protection and privacy, Europe has taken the lead. The GDPR, as a whole, imposes stiff fines on businesses for noncompliance, such as unlawful processing and disclosure of personal data. Countries with comprehensive data protection laws include Australia’s Privacy Act, Argentina’s Personal Data Protection Law, and Canada’s Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA). In the United States, there is a patchwork of federal and state privacy laws based on industry and data type.
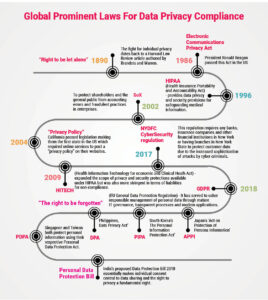
While the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation brought information privacy to the forefront for businesses and consumers worldwide, the roots of privacy laws are deeper than most people realize. In fact, the right to privacy was incorporated into the Universal Declaration of Human Rights by the United Nations in 1948.
Data privacy legislation is constantly being enacted, and the majority of countries around the world have now passed data laws and acts. Which regulations you must follow will depend on where your company operates, what borders you cross, and what industry you are in.
Why is Data Privacy Important?
Being in compliance with privacy policies benefits the brand’s image and value. It instills trust in customers and aids in loss prevention. Apart from that, there are numerous other reasons why data privacy is important for businesses.

- A stringent data privacy compliance policy prevents scrutiny from the consumer as well as relevant public organizations.
- One of the most important reasons for organizations to comply with privacy regulations is to avoid large fines. Those who fail to comply with the privacy regulations risk being fined millions of dollars and facing penalties for years.
- Privacy compliance is now critical for every business due to an increase in the number of regulations, such as the EU’s GDPR and the United States’ CCPA, which protects unauthorized access to critical data.
- A lack of a compliance policy in place can easily lead to data breaches and violations of business ethics. This taints a company’s reputation and brand image.
- Privacy compliance also provides a competitive advantage to the business because clients and customers are more likely to come to them confident in the security of their data.
Data Privacy Framework
According to Cisco’s 2021 Privacy Benchmark Study, organizations with mature privacy programs reap more benefits than the average and find it easier to comply with new privacy regulations. When faced with privacy challenges such as shifting regulatory requirements, conflicting or changing policies/procedures, duplicate compliance efforts, and increased operational costs, many organizations choose a framework. Using a single framework as the foundation for a program alleviates many of these issues and makes it easier to adapt to organizational and regulatory change.
Although a privacy framework is primarily concerned with privacy, it has an impact on many other areas of the organization and may overlap with other frameworks used by other business functions. Involving personnel from various processes, such as cybersecurity, IT, information security, legal, compliance, internal audit, and risk management, as well as key business process owners, may be beneficial. It is critical to include a variety of business functions in the selection process, but it is also critical to establish a decision-making authority.
Whatever framework is chosen, it must support organizational goals, enterprise strategy, and stakeholder needs. If it does not align with any of these elements, it will be difficult to achieve enterprise-wide adoption, limiting the framework’s success. This can be broken down into four sections:
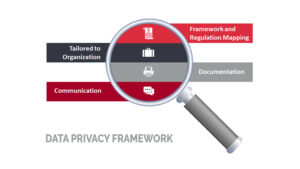
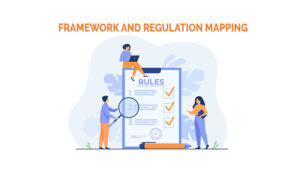
Framework and Regulation Mapping
Several organizations are required to follow the regulations of multiple countries at the same time. In such a case, it is entirely possible that the rules will overlap, resulting in a conflict of interest. If an organization must comply with multiple privacy regulations, you must map out how they interact with your framework and with one another. Furthermore, now is the time to consider any other frameworks that the organization employs to ensure that everything is in sync. Control areas can be mapped out and grouped by regulation and framework to reduce complexity.
Tailored to Organization
Each organization has its own set of privacy risks and regulations. It is advantageous for the organization to lay them out in order to comprehend and fortify those high-risk premises. This entails changing controls to align with specific business functions and the operating environment, which will necessitate input from other departments. Working with other teams to integrate your framework, on the other hand, should help ensure enterprise-wide adoption.
Documentation
The entire process is better documented, from drafting to implementing any privacy compliance. This enables the organization to comprehend and refer to any exception scenarios. It also allows for future changes while keeping the existing policy in mind. Documenting the business reasons for not implementing the control is a good practice. If proper documentation of the scenarios underlying the exception is kept, it will serve as a resource for future audits and assessments.
Communication
When developing or revising a data privacy compliance policy, any organization should involve the core teams. This allows the core teams to not only express their views on regulations, but also to understand the risks as a group. Brainstorming sessions in such scenarios result in more effective and efficient frameworks. It is also critical to communicate any upcoming changes to the organization’s core business teams. It is beneficial to provide appropriate support to teams that may need to make changes as a result of framework adoption.
Data Breach Response Strategy and Plan
Despite strict adherence to data privacy compliance policies, no system is perfect. Cyberattacks and data breaches continue to outwit even the most sophisticated systems. An effective data breach response plan and escalation process can reduce the impact of an intrusion. Employees in charge of breach response should be trained on these plans as well as how to use escalation channels. As proactive preventive measures against a repeat incident, the corrective actions in the response plan must be implemented and documented.

It is not sufficient to know that you are data privacy compliant. You must be prepared to demonstrate your compliance in response to external or internal inquiries. Reports and documentation should make compliance easily verifiable and accessible. Your company should have a process in place for reporting noncompliance, as well as a clear escalation path. Consistent adherence to confidentiality principles should be demonstrated through appropriate monitoring, auditing, and control implementation.
Prominent Data Breaches Across The Globe
- In 2020, India banned 118 Chinese apps for violating Section 69A of the Information Technology Act.
- LinkedIn, the world’s largest professional social media platform, confirmed a massive data breach and the data of over 500 million of its users in April 2020.
- Big Basket reported data breaches and security flaws in their system in April 2021, compromising the sensitive information of over 20 million Big Basket users.
- In 2020, the Solar Wind data breach affected thousands of customers, resulting in a massive data privacy crisis.
In Conclusion..
It is critical that organizations develop strong data privacy compliance policies in order to prevent breaches. Even so, data governance currently faces numerous challenges. One challenge is balancing the privacy of individual data with the use of data for surveillance. Given the rate at which data is multiplying, this ever-expanding database will pose control and management challenges.
Even the increase in international data transfers will necessitate extra caution and new security measures. We still have a long way to go in developing compliance regimes in this sector, owing to its dynamic and ever-changing nature. As a result, it is critical for both consumers and businesses to take privacy compliance seriously and to be prepared for it in the future.
Furthermore, despite the fact that many data protection laws and rules are in place, it is no secret that privacy compliance is complex, and many businesses frequently become lost in the avalanche of legal requirements of these compliances. Due to our involvement with the internet, we will all have to consider privacy compliance sooner or later. What happens to our data and who we should share it with are all important factors to consider.



Comments are closed.