You have likely heard the phrase “blockchain technology” in relation to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin over the past few years. In fact, you might be wondering: “What exactly is it?” As there is no concrete meaning that the average person can readily understand, it appears that blockchain is a platitude, but only in a hypothetical sense.
It is your responsibility to educate yourself on this developing technology so that you are ready for the future when blockchain develops and becomes more approachable. This is the best place to learn the fundamentals of blockchain if you’re new to it. This blog explains all the “whats”, “whys”, and “hows” related to blockchain technology. Let’s go!
What is Blockchain?
Blockchain technology, at its core, is a distributed digital ledger that stores data of any kind. A blockchain can keep track of cryptocurrency transactions, NFT ownership, and DeFi smart contracts. While any traditional database can store this type of data, blockchain is unique in that it is completely decentralized. Blockchain makes it very difficult to hack or cheat the system by distributing identical copies of a database across an entire network.
Let’s take a look at how this complex technology managed to pocket 10% of the global population.
How Does Blockchain Work?
 Blockchain technology is a structure that stores public transactional records, also known as blocks, in several databases, referred to as the “chain,” in a network connected by peer-to-peer nodes. This type of storage is known as a ‘digital ledger.’
Blockchain technology is a structure that stores public transactional records, also known as blocks, in several databases, referred to as the “chain,” in a network connected by peer-to-peer nodes. This type of storage is known as a ‘digital ledger.’
Every transaction in this ledger is authorized by the owner’s digital signature, which authenticates the transaction and prevents it from being tampered with. As a result, the digital ledger’s information is extremely secure. The intriguing aspect is that anyone can see the data, but they cannot corrupt it. This explains the enormous popularity of blockchain and the increased spending on its solution which is anticipated to hit $19 billion by 2024.
Blockchain Use Cases
There are numerous potential applications for blockchain technology in numerous industries. Here are a few typical instances:
- Cryptocurrency: The most common application of blockchain today is as the foundation of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum. The transactions that people make when they buy, exchange, or spend cryptocurrency are recorded on a blockchain. The more people who use cryptocurrency, the more popular blockchain may become.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts, also known as “smart contracts,” are another blockchain innovation. When certain conditions are met, these digital contracts take effect automatically. For example, once the buyer and seller have met all of the deal’s specified parameters, a payment for a product may be released immediately.
- Banking: Blockchain is also being used to process transactions in fiat currency, such as dollars and euros, in addition to cryptocurrency. Because transactions can be verified and processed outside of normal business hours, this may be faster than sending money through a bank or other financial institution.
- Supply Chain Monitoring: Massive amounts of information are involved in supply chains, especially when goods are transported from one part of the world to another. Traditional data storage methods can make it difficult to pinpoint the source of problems, such as which vendor supplied low-quality goods. Storing this data on blockchain would make it easier to track the supply chain, which uses this technology to track food from harvest to consumption.
- Voting: Experts are investigating ways to use blockchain to prevent voting fraud. In theory, blockchain voting would allow people to submit votes that couldn’t be tampered with while also eliminating the need for people to manually collect and verify paper ballots.
- Identity Management: Blockchain technology offers a robust and decentralized method for identity management in the business domain. With its secure and tamper-resistant nature, blockchain allows individuals to maintain full control over their personal identity information while also streamlining the verification procedures. By leveraging blockchain, businesses can enhance the security and efficiency of identity management processes.
- Smart contracts: It enable the automated execution of programmable agreements on the blockchain. They are self-executing contracts that trigger once predefined conditions are fulfilled. This functionality offers businesses the opportunity to automate and enhance the efficiency of various processes, including supply chain agreements, insurance claims, and financial transactions.
How to Become a Blockchain Developer?
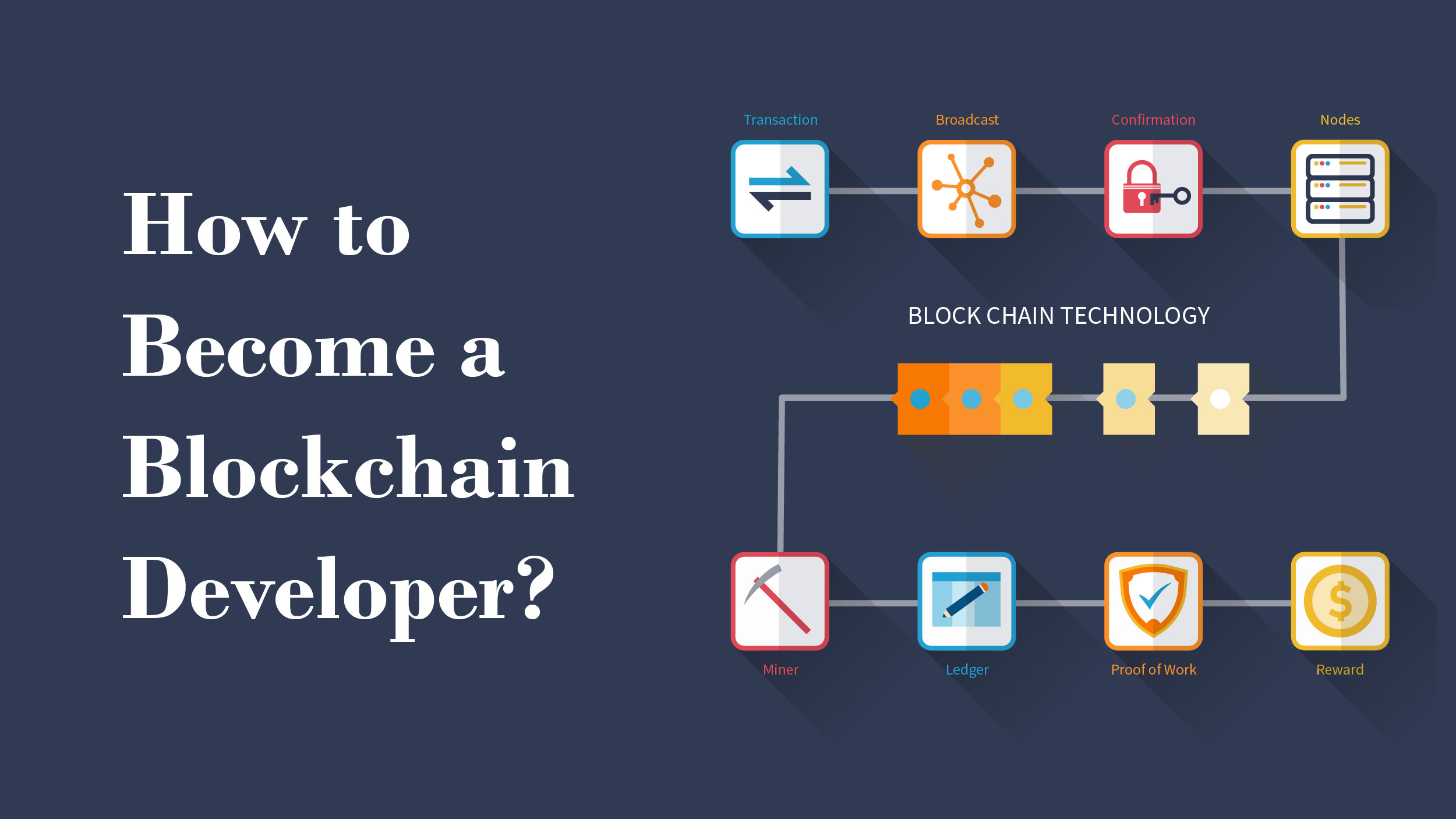 Becoming a skilled blockchain developer involves several key steps:
Becoming a skilled blockchain developer involves several key steps:
- Foundational Understanding: Begin by learning the basics of blockchain technology, including its mechanics and core principles, and explore variations like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Hyperledger.
- Programming Skills: Develop proficiency in programming languages such as C++, Java, Python, Solidity (for Ethereum), and Go. Also, understand data structures, algorithms, and cryptography.
- Blockchain Platforms: Dive into platforms like Ethereum, Hyperledger Fabric, or Corda. Learn smart contract development, network interaction, and how to create decentralized applications (DApps).
- Hands-On Projects: Gain practical experience through hands-on projects, starting with simpler ones and progressing to more complex tasks.
- Community Engagement: Join blockchain developer communities by participating in online forums, meetups, and virtual discussions to exchange knowledge and stay updated on industry trends.
- Specialized Courses: Consider enrolling in specialized courses online or offline to receive structured learning, hands-on projects, and guidance from experts in the field.
- Open-Source Initiatives: Engage in open-source blockchain projects to gain experience, expand your network, and gain recognition in the community.
- Stay Informed: Continuously monitor industry news, study whitepapers, and explore new tools and frameworks to stay up-to-date with blockchain advancements.
- Commitment and Adaptability: Becoming a skilled blockchain developer requires time, dedication, and adaptability in the ever-evolving blockchain landscape. Keep learning and practicing to excel in this field.
Wrapping Up
Blockchain, driven by the rise of Bitcoin and cryptocurrency, is gaining recognition for its numerous practical applications. These applications are being actively implemented and explored, contributing to its growing prominence. With the potential to revolutionize business and government operations, blockchain offers advantages such as enhanced accuracy, efficiency, security, and cost-effectiveness, eliminating the need for excessive intermediaries.
As we enter the third decade of blockchain technology, it is no longer a matter of if established companies will embrace this technology, but rather when they will do so. Currently, we are witnessing a surge in Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) and the process of asset tokenization. As a result, the foreseeable future will be characterized by substantial growth and development within the blockchain realm.



Comments are closed.